Pediatric Epilepsy Syndromes 06
Topic: PediatricCreated on Thursday, October 4 2007 by jdmiles
Last modified on Thursday, October 4 2007.
An 8 year old girl presents to your office. The parents state that the child has been having frequent staring spells. Past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. There is no family history of seizures. Exam is normal. You obtain an EEG, which shows the following finding: 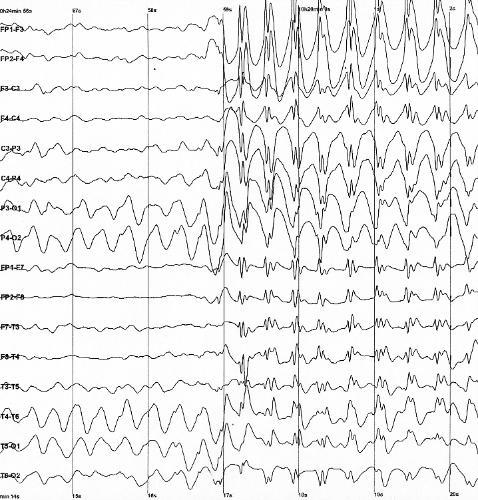 Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons Which seizure types are most frequently seen in this child's epilepsy syndrome?
This question was created on October 04, 2007 by jdmiles.
This question was last modified on October 04, 2007.
ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
A) focal motor, gelastic, and generalized tonic-clonic
This answer is incorrect.
This child has childhood absence epilepsy. Absence seizures are, by definition, seen in this syndrome. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures occur in about 50% of patients. A minority of patients have myoclonic seizures. Gelastic seizures are not associated with this syndrome. Childhood absence epilepsy is a generalized epilepsy syndrome, so focal motor seizures would not typically be seen. ( See References)
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
B) absence and generalized tonic-clonic
This answer is correct.
This child has childhood absence epilepsy. While absence seizures are the sine qua non of this syndrome, generalized tonic-clonic seizures occur in about 50% of patients. A minority of these patients will also have myoclonic seizures. ( See References)
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
C) myoclonic, focal motor, and generalized tonic-clonic
This answer is incorrect.
This child has childhood absence epilepsy. Absence seizures are, by definition, seen in this syndrome. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures occur in about 50% of patients. A minority of patients have myoclonic seizures. Childhood absence epilepsy is a generalized epilepsy syndrome, so focal motor seizures would not typically be seen. ( See References)
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
D) absence, generalized tonic-clonic, and gelastic
This answer is incorrect.
This child has childhood absence epilepsy. Absence seizures are, by definition, seen in this syndrome. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures occur in about 50% of patients. A minority of patients have myoclonic seizures. Gelastic seizures are not associated with this syndrome. ( See References)
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
E) absence, generalized tonic-clonic, and infantile spasms
This answer is incorrect.
This child has childhood absence epilepsy. Absence seizures are, by definition, seen in this syndrome. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures occur in about 50% of patients. A minority of patients have myoclonic seizures. Infantile spasms are not associated wtih this syndrome. ( See References)
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
References:
| 1. Levin, K.H., and Luders, H.O. (Eds.) (2000). Comprehensive Clinical Neurophysiology. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia.
| |
| 2. Trescher, W.H., and Lesser, R.P. (2004). The epilepsies. In Bradley, W.G., Daroff, R.B., Fenichel, G.M., and Jankovic, J. (Eds.). Neurology in Clinical Practice, Fourth Edition. Butterworth Heinemann, Philadelphia, pp. 1953-1992.
| |
|
 |  |  | 
|  |  | | Please log in if you want to rate questions. |
FrontalCortex.com -- Neurology Review Questions -- Neurology Boards -- Board Review -- Residency Inservice Training Exam -- RITE Exam Review
pediatric
Pediatric Epilepsy Syndromes 06
Question ID: 100407067
Question written by J. Douglas Miles, (C) 2006-2009, all rights reserved.
Created: 10/04/2007
Modified: 10/04/2007
Estimated Permutations: 8400
0 user entries
|
|